Test geek and founder of Aptitude-Test-Prep.com
What Is the EEI MASS Test?
The EEI MASS Test (Power Plant Maintenance Positions Selection System) is a pre-employment assessment battery used to screen power plant maintenance positions. The test is designed and administered by the Edison Electric Institute (EEI).
The EEI MASS assesses 4 cognitive abilities designed to evaluate how well a candidate will perform on maintenance jobs.
Test Structure and Question Format
The EEI MASS Test is divided into 4 sections, each with its own content and time limit:
- Assembling Objects – 20 questions in 15 minutes.
- Mathematical Usage – 18 questions in 7 minutes.
- Mechanical Concepts – 44 questions in 20 minutes.
- Reading for Comprehension – 36 questions in 30 minutes.
Let’s describe each of these sections in a bit more detail.
You will find detailed answers for the questions below (+more) in the Free Practice section.
Assembling Objects
The Assembling Objects section assesses your spatial reasoning abilities. The questions in this section include a disassembled object that you should visualize in its assembled form. Dots with letters indicate where each part should go.
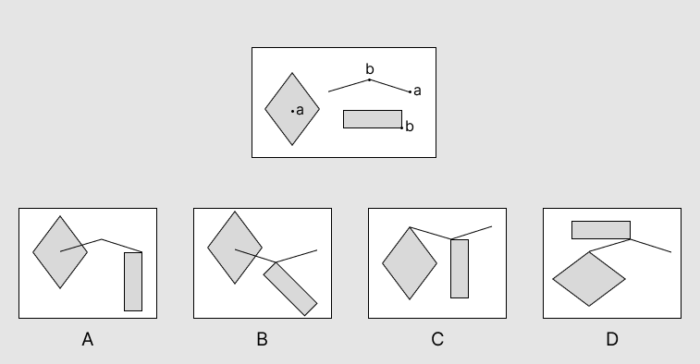
Mathematical Usage
The Mathematical Usage section assesses your ability to calculate quickly and accurately via unit conversion questions. You have 7 minutes to solve 18 questions.
Pro Tip
The Mathematical Usage section is probably the section in which time poses the greatest challenge. Focus on improving your solving speed to succeed.
Mechanical Concepts
The questions in the Mechanical Concepts section assess your understanding of basic mechanics and electricity. The questions do not require calculations, and therefore can be solved quickly. The section contains 44 questions to be solved in 20 minutes.
Pro Tip
The variety of questions in the Mechanical Concepts section requires you to understand the major physical principles at the heart of the test. Examples are law of the lever, centrifugal force, fluid mechanics, etc.
Reading for Comprehension
The last section measures your ability to understand and interpret text. You will be presented with a short piece of text (~400 words) and will be required to answer 9 questions about it.
4 such texts will be given throughout the section, so 36 questions overall. The total time limit is 30 minutes.
EEI MASS Test Preparation
If you want to prepare for the EEI MASS test, I recommend JobTestPrep’s MASS Test Preparation.
- A diagnostic test to identify your weaker areas
- Covers all sections of the actual test
- A money-back guarantee policy
What Do You Get?
- Diagnostic Test + Interpretation Guide
- Full-length EEI MASS tests
- Math Usage – Units practice test
- Mechanical Aptitude practice tests
- Assembling Objects practice tests
- Reading Comprehension practice tests
- Video Tutorial – how to solve verbal questions
- 2 Mechanical & Spatial Reasoning guides
Start Preparing Now
Full Disclosure: I am affiliated with JobTestPrep. Clicking the links helps me provide you with high-quality, ad-free content.
Test Interface
The MASS test interface is easy to follow and is similar to that of other EEI tests such as CAST, TECH, or POSS. Here are 4 basic things you should know about the test:
Separate Sections
Each section on the EEI MASS Test is conducted separately, with its own content and time limit. This means that you will not be able to use spare time from longer sections such as Reading for Comprehension (30 minutes) for shorter sections like Mathematical Usage (7 minutes). Make sure you are well-prepped for each section’s specific time constraints.
You Can Move Between Questions
The MASS test allows you to move back and forth between questions or skip them and get back to them later. That allows better time management and development of solid solving methods while preparing.
No Points Reduced for Wrong Answers
The MASS Test, as all of EEI’s tests, does not reduce points for wrong answers. So, if you don’t know the answer, it’s better to guess than not to answer at all.
Calculators Are Not Allowed
Only 18 questions out of the test’s 118 require calculations, so it’s not as major of an issue as you might think. However, since calculators are not allowed, make sure you have mastered pen-and-paper calculation to maximize your chances of success.
Free Practice
This free practice test includes 10 questions, and is designed to get you familiar with the types of questions on the EEI MASS Test and their level of difficulty.
You will also find answers, explanations, and tips for success.
Good luck!
Section 1 – Assembling Objects
Question 1
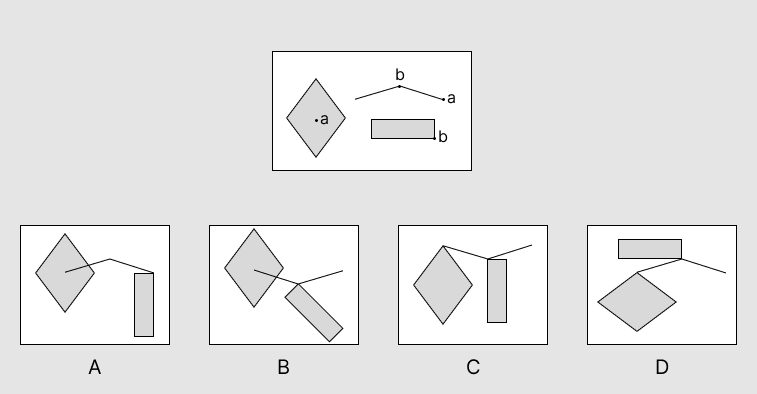
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is B.
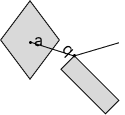
Question 2
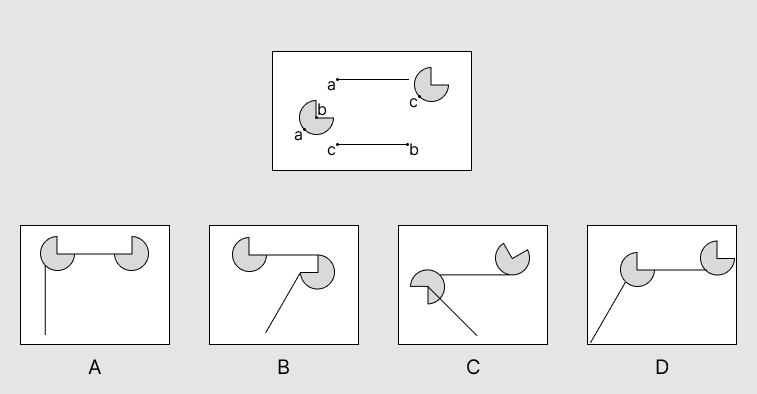
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is D.

Section 2 – Mathematical Usage
Question 3
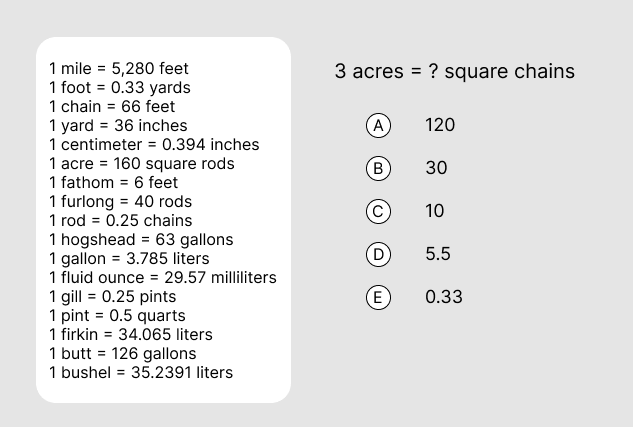
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is B.
3 acres = [3 x 160] square rods = [3 x 160 x (0.252)] square chains = 30 square chains.
Pro Tip
When converting square units – don’t forget to square!
Question 4

Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is C.
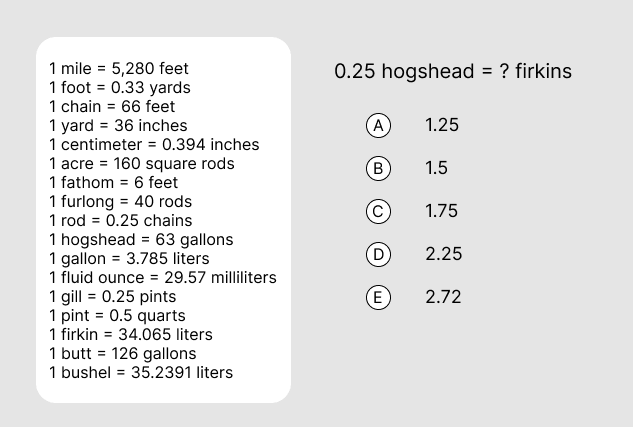
0.25 hogshead = [0.25 x 63] gallons = [0.25 x 63 x 3.785] liters = [0.25 x 63 x 3.785 x (1/34.065)] firkins = 1.75 firkins.
Question 5

Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is A.
8 fathoms = [8 x 6] feet = [8 x 6 x (1/66)] chains = [8 x 6 x (1/66) x (1/0.25)] rods = [8 x 6 x (1/66) x (1/0.25) x (1/40)] furlongs = 0.73 furlongs
Section 3 – Mechanical Concepts
Question 6

Answer and Explanation
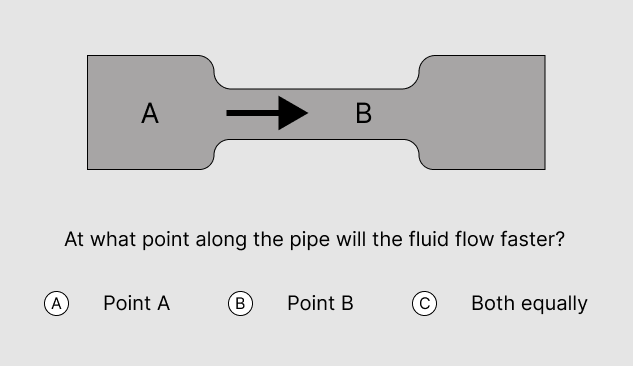
The correct answer is B.
In a pipe where the flow is uniform, the narrower the pipe, the faster the flow. The underlying physical principle is the volumetric flow rate formula.
Q = V x A
- Q = volumetric flow rate
- V = flow velocity
- A = pipe cross-section area
Since Q is constant along the entire pipe, if A is lower, V must be higher.
Pro Tip
While the mechanical concepts section does not require previous knowledge, being familiar with basic physics is going to give you a major advantage.
Question 7
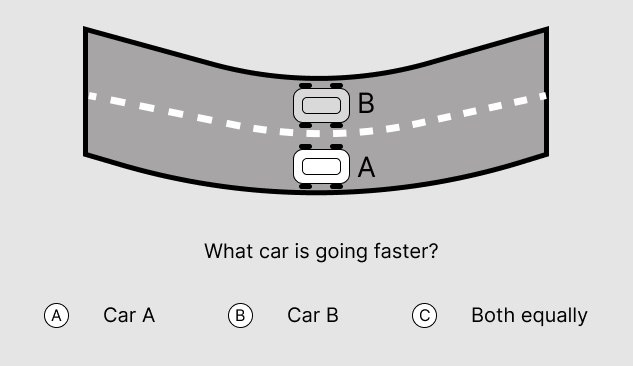
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is A.
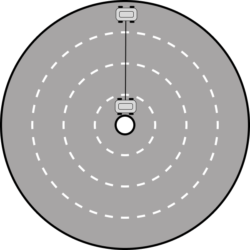
When two cars travel side by side, the one doing the larger curve is going faster. The underlying physical principle is angular and linear velocity.
V = w x R
- V = Linear velocity (how fast the car is moving in a straight line)
- w = Angular velocity (how fast the car is “rotating” along the center of the circle)
- R = The distance from the imaginary center of the circle.
Since Car A and Car B have the same angular velocity (they travel side by side), but Car A is farther from the center, its linear velocity is greater.
Tip: If you still haven’t wrapped your head around this, think about a VERY wide circle, with two cars travelling inside, with a line between them. Clearly, the car in the outer lane will have to travel much faster than the one in the outer lane to keep up.
Question 8
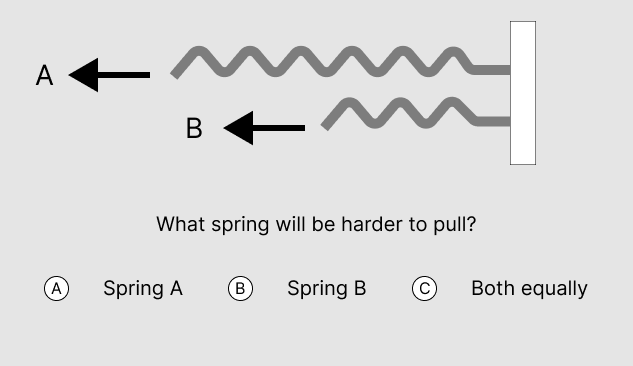
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is B.
A spring’s stiffness is proportional to its length. The longer the spring, the less stiff it is. The underlying principle is Hooke’s Law.
Section 4 – Reading for Comprehension
Use the following passage for questions 9-10.
Safety Measures in Electrical Work
Electricians work with potentially hazardous electrical systems, and ensuring their safety is paramount to prevent accidents and injuries. Implementing effective safety measures is crucial in minimizing risks and creating a secure working environment.
Wearing appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is fundamental for an electrician’s safety, including insulated gloves, safety glasses, flame-resistant clothing, and steel-toed boots. PPE provides a protective barrier against electric shocks, burns, and other potential hazards. However, proper safety measures are designed to ensure that PPE remains only a backup plan.
Using the right tools for the job is crucial in that sense. Insulated and non-conductive tools help prevent electric shock, and regular maintenance ensures that tools remain in good working condition. Compliance ensures that electrical installations meet safety standards, reducing the risk of accidents and ensuring the longevity of the electrical systems. Having first aid kits, fire extinguishers, and other equipment in the worksite ensures a prompt and effective response in case of accidents or injuries.
Professional knowledge is an essential component of safe work. Hence, electricians must undergo proper training and obtain the necessary certifications. While in the case of other jobs this training is designed mostly for professional reasons, the electrician codes and regulations were designed to prevent serious injury and death. Therefore, an in-depth familiarity with them is non-negotiable in this case. This requirement translates to a legally mandated official certification in nearly all countries and states, yet the specifications may vary. This includes but is not limited to adequate knowledge of electrical systems, safety protocols, and emergency procedures. Some regulatory bodies also require first aid training.
As every working environment has its own unique features, a thorough risk assessment should be carried out by a certified electrical engineer or electrician before commencing any electrical work. Identifying potential hazards and implementing preventive measures ensures a safer work environment, including assessing the voltage levels, potential exposure to live circuits, and any other factors that may pose a risk.
The usage of lockout/tagout procedures is another highly important safety measure. These procedures involve isolating energy sources and using locks or tags to protect electricians from unexpected electrical discharges. De-energization of panels should be used whenever possible, as well as proper labeling of circuits for quick and accurate identification.
Additional safety measures should be implemented for electrical work at heights. This may include the use of harnesses, guardrails, and proper scaffolding. Implementing these measures helps prevent falls and the associated injuries. Safety organizations and labor unions regularly conduct training and certification plans for those working at height.
Question 9
In which paragraph would it be most relevant to describe new patented pliers especially designed for electricians?
- Paragraph 1
- Paragraph 2
- Paragraph 3
- Paragraph 4
- Paragraph 5
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is C.
Each paragraph of the text deals with a different aspect of safety measures for electricians. Paragraph 3 focuses on “the right tools for the job”, a category that is most appropriate for pliers. Paragraph 2, which describes Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), is less relevant, as it focuses on equipment whose main purpose is to protect the electrician.
Question 10
Which of the following measures could be described as “the last line of defense” in an electrician’s work?
- Risk assessment
- An official certification
- Proper work tools
- PPE
- Professional knowledge
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is D.
According to the text: “proper safety measures are designed to ensure that PPE remains only a backup plan.” That is, if all other safety measures have failed, PPE is the last resort to prevent injury or death. Careful adherence to safety protocols should ensure that electricians do not face a situation in which their safety depends on their PPE.
EEI MASS Test Preparation
If you want to prepare for the EEI MASS test, I recommend JobTestPrep’s MASS Test Preparation.
- A diagnostic test to identify your weaker areas
- Covers all sections of the actual test
- A money-back guarantee policy
What Do You Get?
- Diagnostic Test + Interpretation Guide
- Full-length EEI MASS tests
- Math Usage – Units practice test
- Mechanical Aptitude practice tests
- Assembling Objects practice tests
- Reading Comprehension practice tests
- Video Tutorial – how to solve verbal questions
- 2 Mechanical & Spatial Reasoning guides
Start Preparing Now
Full Disclosure: I am affiliated with JobTestPrep. Clicking the links helps me provide you with high-quality, ad-free content.
















